


Author:Tang Yuwen,Director, Research Office of Hunan Committee of Chinese People's Political Consultative Conference (CPPCC)
On the morning of June 1, 2022, a report entitled "Strengthening the Provincial Capital, Promoting the High-quality Economical Development for Hunan Province" given by Tang Yuwen was held in the lecture hall of Tongxin Building of Hunan Institute of Socialism, Changsha. As one of the important reports of The 7th Provincial Elite Training Class for Returned Overseas, it includes three parts-the logical thinking, the realistic basis and the implementation path.

Tang Yuwen
Director, Research Office of Hunan Committee of Chinese People's Political Consultative Conference (CPPCC)
Vice Chairman, Hunan Federation of Social Sciences
Former Deputy Director, Development Research Center, Hunan Provincial Government

Tang’s lecture in the conference hall, Tongxin Building, Hunan Institute of Socialism
Part 1. Logical thinking of strengthening provincial capital
On April 19, 2022, the CPC Hunan Provincial Committee and the Hunan Provincial People's Government issued Several Opinions on Implementing the Strategy of Strengthening the Provincial Capital to support the high-quality development of Changsha City. Why the development of Changsha City must be strengthened? Tang stressed the following reasons to answer the concern according to World Development Report (2009).
Firstly, there has been an inevitable trend of economical concentration, 1/4 of the world’s GDP produced by regions accounting for only 0.3% of the world’s land area, half by 1.5% and 90% by 16%.
Secondly, the living standards between the economic intensive and non-intensive areas converge are convergent, i.e., in Japan, the three metropolitan areas have concentrated 73.6% of the country's GDP, but they have also concentrated 68% of the national population, and the per capita GDP is only 1.08 times that of the whole country.
Thirdly, various resources continue to concentrate in big cities. The world is becoming more and more urbanized, and the economic sector is increasingly concentrated in the densest urban central areas. In 1900, the total population of the world's 100 largest cities accounted for only 4.3% of the world's population, while at present, it accounts for 7.5% of that. With the further development of the country, the number of the migration to cities and their suburbs is increasing as their density increases (See fig.1).
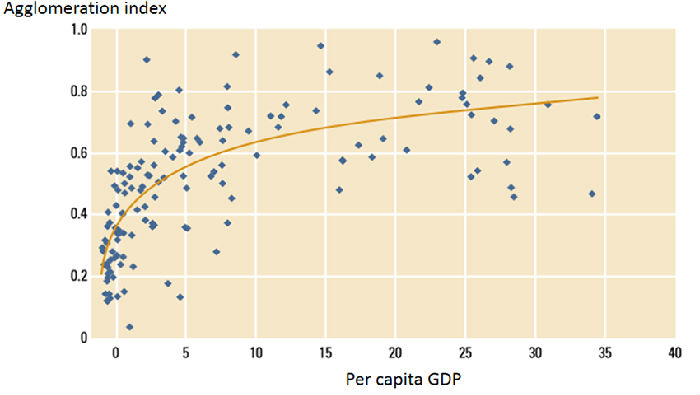
Fig.1 The population is concentrated in urban areas with the development of the country
People perhaps ask whether strengthening the development of Changsha will hinder the integration process of Changsha, Zhuzhou and Xiangtan (CZT) or not, Tang explained that in the process of the economic integration of CZT, strengthening the development of provincial capital Changsha would radiate and drive the other two cities, and then promote the leapfrog development of the integration of CZT Urban Agglomeration.
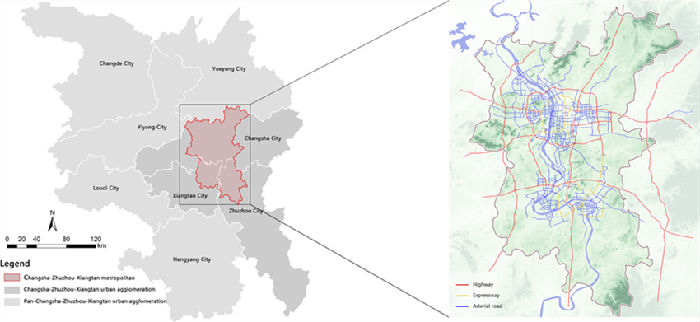
Fig.2 Location Map of Changsha Zhuzhou Xiangtan Metropolitan Area
Source: Jian Zheng,et.al. (2020)
Part 2. Realistic basis of strengthening provincial capital
According to the evidence from China Statistical Yearbook of related years, Tang made an overall introduction to the development situation of Changsha, and found that Changsha was generally in a medium position compared with Guangzhou, Chengdu, Wuhan, Zhengzhou and Xi'an; it was indeed ahead of the other five in terms of housing, education and economy, but at a medium level in capital, medical treatment and science and technology. Moreover, he added, it lagged behind the five cities concerning openness, population, area and transportation. (See fig.3)
Among the factors affecting urban development, population is an important basis for Hunan to implement the strategy of strengthening the provincial capital. Tang showed that the total population of Changsha had exceeded 10 million, ranking fifth in population increment (3.069 million), and fourth in annual growth rate (3.62%). The population potential of Changsha was relatively strong, with only 15.12% of the population primacy degree, lower than that of Xi'an, Chengdu and Wuhan, but there was still growing space of about 3.2 million people, he stressed. (See fig.4 and fig.5)
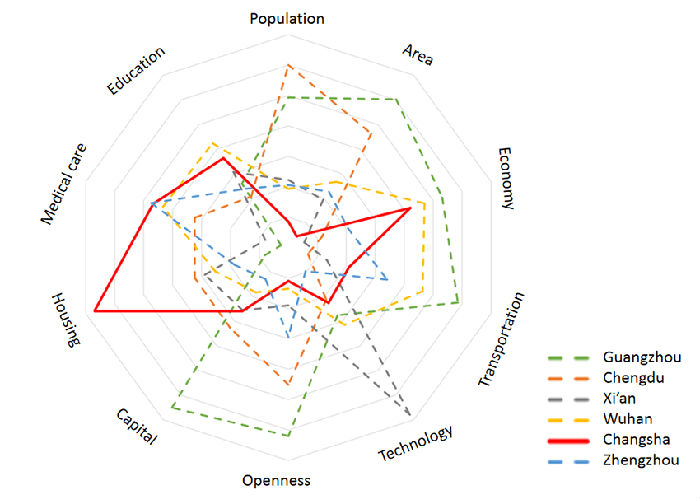
Fig.3 Comprehensive comparison of six cities in 2020
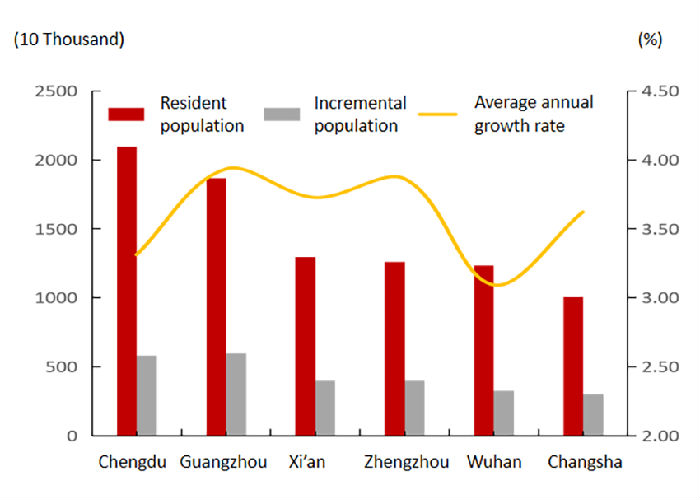
Fig.4 Comparison of resident population in 6 cities (2020)
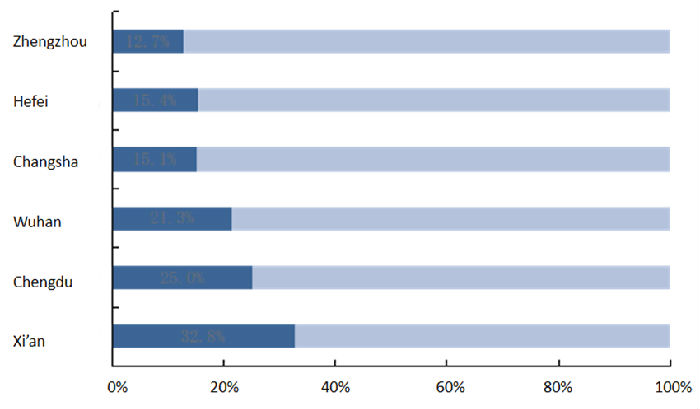
Fig.5 Comparison of population primacy in 6 cities (2020)
In terms of developing space, Tang mentioned that the urban development progress of Changsha was relatively slow, with 414.1 square kilometers of construction land and 474.8 square kilometers of built-up area, significantly lower than the other five cities, and thus there was great potential for space expansion, he explained, Changsha covers a total area of 11,819 square kilometers, only smaller than Chengdu (14,335 square kilometers) among the six cities, the vast urban area provides a strong guarantee for urban expansion. In addition, he added, there was close urban communication among Changsha, Zhuzhou, and Xiangtan, by innovating the mechanism of regional trusteeship and joint management, he believed that the development space of Changsha can be expanded effectively.
In terms of economic growth, Tang continued, Changsha had strong development potential, its GDP growth in 2021 was 1.32 trillion yuan, ranking 15th of China; the actual growth rate was 7.5%, slightly lower than the national average growth rate of 8.1%. From the long-term perspective, he said that Changsha's GDP had successively overtaken Zhengzhou, Fuzhou, Shijiazhuang and other cities from 2001 to 2020, rising by 12 steps in the country’s ranking. (See Table 1)
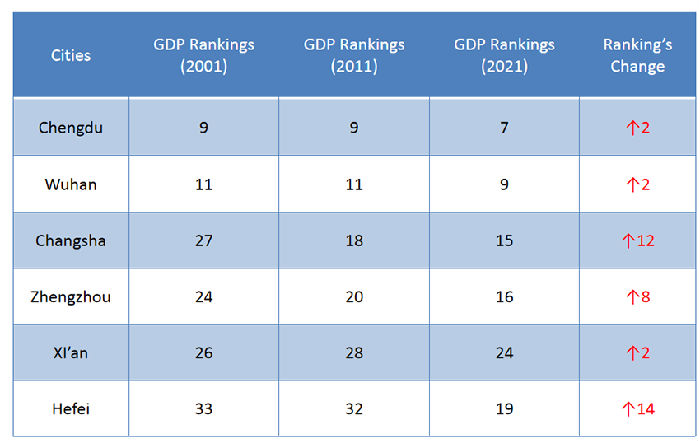
Table 1. GDP ranking change of six cities
Changsha's scientific and technological innovation ranks the first echelon in China, and has been ranked in the top 10 for two consecutive years. Its R & D expenditure has increased rapidly, but there is still a big gap between the total amount and the leading cities. Traditional innovation platforms are very rich, but new platforms are insufficient. The output of innovation achievements is efficient, ranking among the top five in China.
Furthermore, Changsha has strong competitiveness among the six cities in terms of open exchanges, capital allocation, housing supply, medical supply and education supply, which provides a foundation for the implementation of the strategy of strengthening the provincial capital.
Part 3. Implementation path of strengthening the provincial capital
Finally, Tang systematically introduced the overall factual path of the strategy of strengthening the provincial capital through the policy interpretation of the Hunan provincial government, respectively, improving the core functions of the provincial capital, strengthening modern industries, creating a strategic platform, stimulating market vitality, improving the quality of the city, continuously enhancing Changsha's provincial radiation, regional leadership, national competitiveness and global influence, and striving to make Changsha's regional GDP reach about 2 trillion yuan by 2026, with a permanent population of more than 12 million, and more than 30% of the city's economy. The per capita disposable income of urban and rural residents would reach 80000 yuan, and the main indicators of high-quality development would rank the top among the provincial capitals in China, significantly enhancing the driving and radiating effect on the integration of CZT and the coordinated development of the other cities in the province.
Tang's wonderful lecture came to end with bursts of applause, the attendees actively communicated with him on specific issues to seek the new development of Changsha, as well as the new leap of Hunan. It is believed that the strategy of strengthening the provincial capital issued by Hunan is going to bring new development opportunities to the other cities of Hunan.
Edited, translated and reported by Chai Ning