


Author: Liu Peng, Zhang Ning
Huazhong University of Science and Technology
Slow transportation system is in a relatively weak position in the urban transportation system, usually after the completion of the urban road transportation system planning, which puts forward from the city level, with a insufficient consideration of physical and spatial environment characteristics of the city itself, lacking enough connections between upper and lower levels of planning and "bottom-up" feedback, resulting in the difficult implementation of the planning content.
Concentrated in urban parks, commercial blocks, and other key urban areas, with leisure and tourism as the main purpose, most slow transportation system practices ignore the consideration between key urban areas and surrounding functional areas and urban residential areas, which is one of the reasons why parking difficulties, traffic congestion, and reduced willingness to travel occures in key urban areas and have not been alleviated.
In the practice of the slow transportation system, there are problems of "pursing quick success" and extensive promotion, but lack of long-term planning. For example, neglecting the construction of non-motor vehicle parking spaces and other supportive infrastructures, the construction of building the sense of slow traffic places, as well as reasonable and efficient policy system will lead to the poor practical results of the slow transportation system and the continuous reduction of space quality.
3 Research scope and technique
3.1 Research scope
The study is located in the area spatially enclosed by the second ring road of Wuhan with three linear elements of the Han River and the Yangtze River, about 68 square kilometers, involving three municipal districts: Jiang'an District, Jianghan District, and Qiaokou District. There are two important ecological landscape resources of the Yangtze River and the Han River in the study area, as well as urban parks, such as Zhongshan Park, Jiefang Park and Lingjiao Lake Park. Due to the enclosed management, scattered spatial distribution and the lack of system integration, accessible park resources cannot effectively improve the quality of urban living environment. At the same time, the area also covers newly and previous developed urban areas, small blocks, dense road networks, and large-scaled urban streets coexist, with prominent problems like mixed land use, traffic congestion, contradictions between people and vehicle, and reduced living quality.
3.2 Research technique
On the basis of the built-up urban area, planning the slow transportation system needs to subtly sort out the inherent material spatial characteristics of the city, so as to create a compatible and effective slow transportation system.
4 The exploration of slow transportation system based on the urban spatial characteristics
4.1 "Traffic fence" identification based on road condition data
The contradiction of road occupancy of people and vehicles has always been the most significant problem in the practice of slow transportation system, also the separation of job and housing makes fast and stable vehicle traffic equally important for commuters. The urban transportation planning cannot be unilaterally simplified into "people-oriented" or "vehicle-oriented" traffic, which makes the order of traffic flow the priority of traffic flow. Therefore, the planning of slow transportation system should promote the orderly operation of urban traffic flow through reasonable planning and design schemes, on the basis of respecting the existing traffic flow characteristics of the city. This paper uses the Baidu Map API interface to hourly obtain Baidu road condition information on weekdays and weekends, and identifies the "traffic fence" in the physical spaces of the city. The condition of the road traffic was divided into five levels, namely smooth, basically smooth, slow, congestion, and severe congestion. The more congested the road traffic is, the greater the road traffic carrying capacity has, the less safety the road has. (Figure 1 and 2)
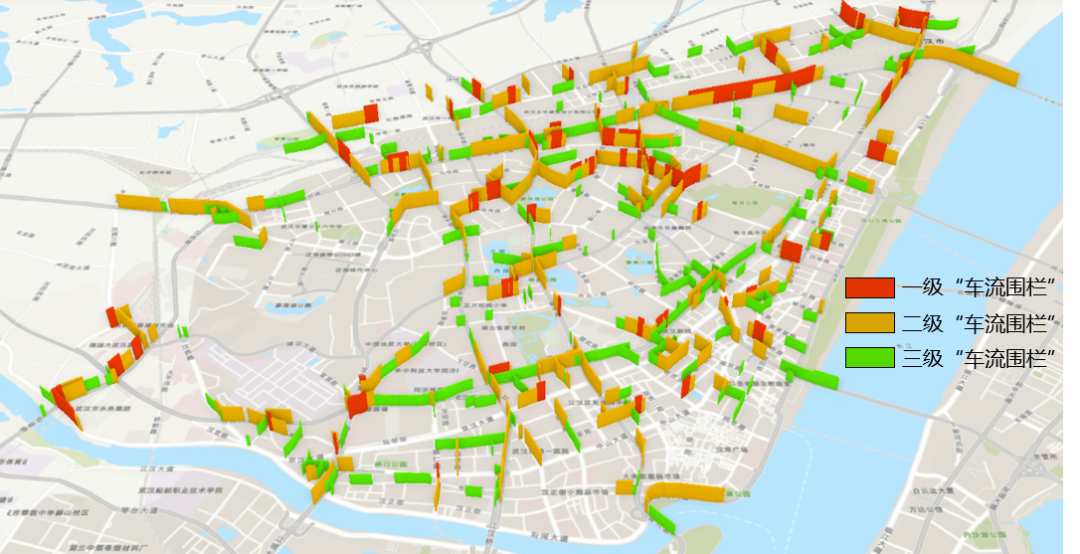
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of road condition information of nodes at typical working days
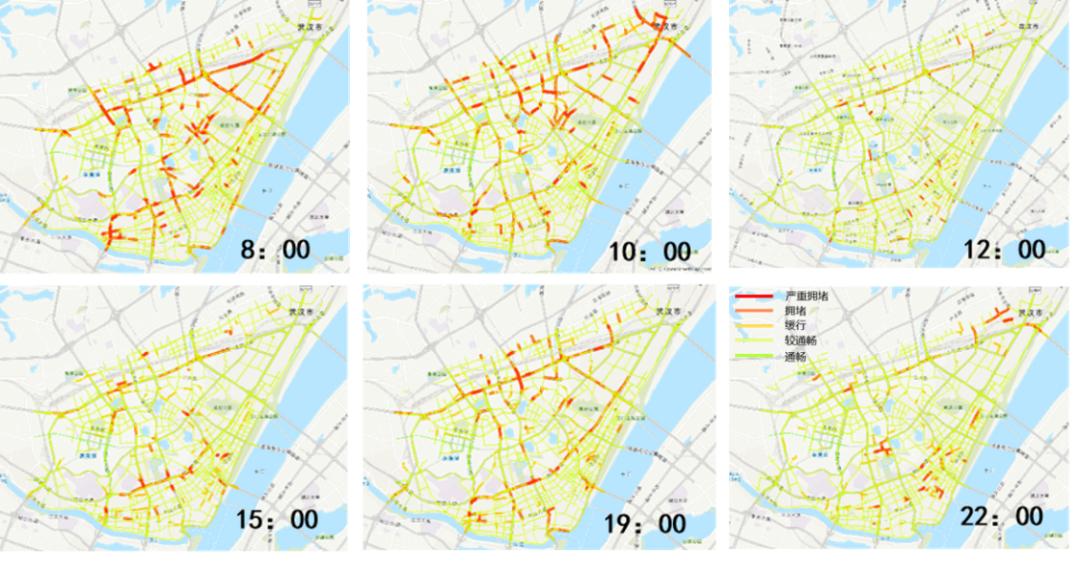
Fig. 2 Schematic diagram of road condition information of nodes at typical weekends
In order to predict the maximum probability of road congestion, this paper obtains the comprehensive "traffic fence" results of the study scope by analyzing the road traffic data for each hour of weekdays and weekends through spatial overlay analysis method. The final result is divided into five levels according to the natural break point method, and the first three levels are taken as the final "traffic fence", and the result is shown in Figure 3.

Fig.3 Schematic diagram of the construction of the three-level "traffic fence" within the research scope
4.2 Street structure feature recognition based on spatial syntactic model
Based on the assumption that people spatially move freely, spatial syntax is originated from the exploration of the relationship between the function and form of constructions. Through mathematical models, spatial syntactic model studies he composition of space to judge the correlation between space composition and functions. Therefore, based on the theoretical assumption that urban space is self-organizing, spatial syntactic model is also applicable to analyse of urban spatial form and structure. Take city streets as linear spaces enclosed by urban buildings, and since the length of streets, street spaces are extended to line features in the spatial syntactic model.
4.3 Evaluation of street space slow traffic quality based on multi-source data
The practice of urban slow transportation system mostly occurs in the process of urban renewal, because as a linear spatial element within the city, it often involves larger urban spaces, more government agencies and stakeholders. Therefore, on the basis of full understanding of the spatial quality of urban streets, it is significant to save costs, promote project progress, and improve the quality of human settlement environment by formulating suitable slow transportation system practice plans according to local conditions to avoid subjectivity and randomness in scheme design. This paper evaluates the slow traffic quality of street space from two aspects: comfort and convenience. Through the Baidu API interface, the street view image data within the research scope is obtained, and then the street green view rate and sky ratio are identified by the method of picture semantic segmentation, and the sum of the green view rate and the sky ratio represents the comfort of the slow driving quality of the street space (the higher the value, the more suitable for slow traffic in the streets) (Figure 4).
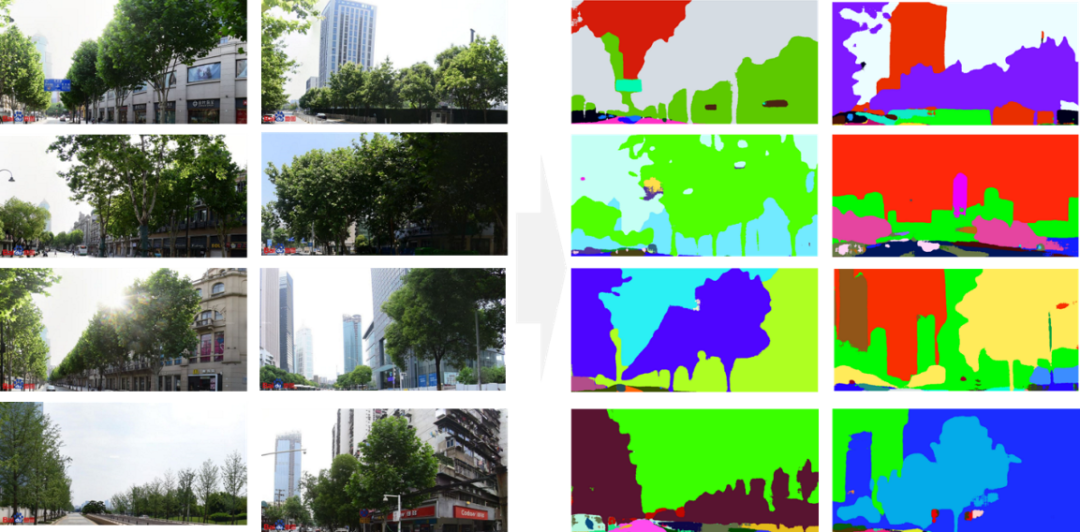
Fig. 4 Example of Semantic Segmentation of Street View Pictures
4.4 Research scope: construction of slow transportation system
In the planning practice of slow traffic system, it should be based on the analysis results of urban material and spatial characteristics, and attention should be paid to avoiding intersection with the "traffic fence" plane in the planning of slow travel routes, causing traffic disorder. The main slow traffic routes in the same area give preference to street spaces with high comfort and convenience. In the selection of nodes in the slow-moving spaces, the streets with high spatial syntactic integration should be based on the streets, and the neighborhoods with high spatial quality of urban streets should be considered as the key areas for construction. In addition, we should pay attention to the reasonable organization of slow traffic flow, and at the same time, set up appropriate node places.
05 Conclusion and discussion
At present, people's needs of travelling through slow transport play a decisive role in the planning practice of slow transportation system, and ignoring the physical and spatial characteristics of the city also has an important impact on the construction of slow transportation system. There are also two extremes of urban slow transportation system planning practice—the scale of planning at the city level is too large, making it difficult to implement the planning content, while the scale of the block is too small, which limits the ability to improve the quality of the urban environment. In order to solve such problems, this paper aims to explore the physical spatial characteristics of the city, obtain real-time road condition information through network programming technology, construct the "traffic fence" of the city, obtain street view image data and POI data to identify the slow transport quality of street space, construct a spatial syntactic segment model to analyze the structural characteristics of urban road network. Based on the analysis results of urban physical spatial characteristics and the ecological environment elements of the research scope itself, the slow transportation system within the research scope is finally constructed from the perspective of urban material spatial characteristics, which better makes up for the shortcomings in the planning practice process of the slow transportation system.
Source: <https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/qWShu17qypW0r0oEpUgkvg>
Translated by Zhang Chenxi