



1 General Provisions
1.1 Basic Concept
A low-Carbon pilot district (hereinafter referred to as "pilot district") refers to a certain scale and functionally comprehensive urban area in the new city. The pilot zone realizes carbon emission monitoring and constraint management in the whole life cycle of urban planning and construction through many measures such as scientific and integrative planning, low-carbon sequential construction and innovative and fine management.
1.2 Guiding Ideology
Guided by Xi Jinping's thought of ecological civilization, the pilot zone will focus on promoting the national strategy of Emission Peaking and Carbon Neutrality, fully implementing the "Cooperation Framework Agreement on Building a Chinese Model for the Refined Construction and Governance of Mega Cities", exploring new paths of green and low-carbon planning and construction management, providing and demonstrating green and low-carbon development for Shanghai and the whole country, and strongly promoting the construction of ecological civilization.
1.3 General Objectives
The objectives of the project are to clarify the regional boundary and low carbon development goals of the pilot area, establish scientific and reasonable carbon emission statistics, monitoring and accounting mechanism, effectively reduce the carbon emissions of the pilot area, and make the carbon emission intensity of the pilot area reach the advanced level of similar areas in the city after the establishment period. The guidelines can regulate and guide the planning and management construction work of the pilot zone, improve the scientific, rationale and operability of the planning and construction of the pilot zone, and accumulate mature experience that can be replicated and promoted.
1.4 Basic principles
1) Low-carbon orientation
The guidelines focus on reducing carbon emissions and increasing carbon sinks, so as to propose relevant planning and construction guideline measures and lead to the formation of a technical path for the whole process of low-carbon construction in the pilot area.
2) Focus on people's experience
In terms of indicator setting and construction guidance, the guidelines take into account people's experience and sense of well-being by linking to the construction of the "15-minute community living circle".
3) Quantitative guidance and control
In terms of guidance, the guidelines set quantitative carbon reduction targets, identify key indicators of carbon reduction in the pilot area in general and in sub-dimensions, and ensure the measurability of these indicators.
4) Reasonable and Dynamic Indicators
The guideline is benchmarked against the advanced level of carbon emission governance, and it enhances the rationality of indicator guidance construction by combining a dynamic real-time feedback indicator adjustment system.
5) Indicator System
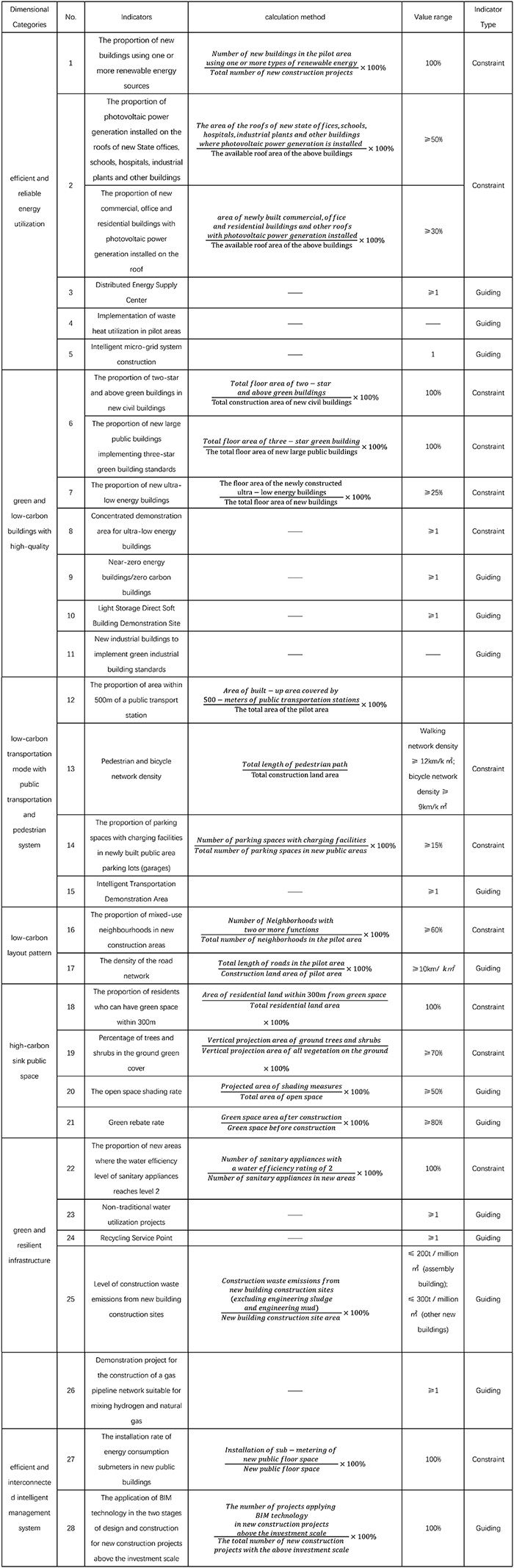
Based on carbon emission sources, this guideline has developed a carbon reduction key indicator system consisting of 7 dimensions: efficient and reliable energy utilization, green and low-carbon buildings with high-quality, low-carbon transportation mode with public transportation and pedestrian system, low-carbon layout pattern, high-carbon sink public space, green and resilient infrastructure, and efficient and interconnected intelligent management system.
Source: <https://zjw.sh.gov.cn/jsgl/20220301/4f85d9ad98954bee9004a0d6d529f086.html>
Edited and translated by Hou Ying