



The 15th meeting of the Conference of the Parties to the United Nations Convention on Biological Diversity (COP15) kicked off in Kunming, Southwest China's Yunnan Province, on October, 11 and on the afternoon of October 14, 2021, the Ministry of Natural Resources released “Typical Cases of Ecological Restoration in China” (including 18 cases) at the Theme 4 - “On Ecological Protection and Restoration Based on Natural Solutions” of Ecological Civilization Forum of COP15. The 18 cases are selected from the 127 nominated ecological restoration projects by relevant ministries, provincial natural resources authorities and the commonweal organizations. These cases aim to show the diversity of ecosystem, typical problems on ecosystem and comprehensive methods of ecological restoration.
Case 1: The Mechanical Forest Field of Sehan Dam
Located in northern China's Hebei Province, the Mechanical Forest Field of Sehan Dam was founded in 1962. Sehan Dam was once a royal retreat thanks to its cool summer weather and hunting area, however, the region turned into a desert by the end of the Qing Dynasty due to forest fires, deforestation and constant wars. Heavy northern winds from neighboring Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region worsened the situation. The expansion of the desert also led to Beijing grappling with decades of sandstorms, which seriously threatened the capital’s environment.
Over 350 foresters were first sent to the region to fight the desertification as early as the 1960s. After 55 years of efforts by three generations of experts, Sehan Dam has become the largest man-made forest park in the world. The canopies have also brought rich natural resources, such as carbon sequestration, water resource restoration and rich forestry resources. Compared with the initial period, the area of forest land increased by 3.8 times, the amount of forest accumulation increased by 30.4 times, and the forest coverage increased from 11.4% to 82%. The average number of windy days per year decreased from 83 to 53 days, and the average annual rainfall increased from less than 410 mm to 479 mm. For one year, Sehan Dam can hold water sources and purify water 284 million cubic meters, absorb 860.3 million tons of carbon dioxide and produce 598.4 million tons of oxygen. The forests contribute to more than 60 million RMB total income per year and help more than 1200 households and more than 10 thousand residents cast off poverty to get rich. These achievements will greatly help improve north China’s ecosystem.

Before and after comparison of ecological restoration of Sehan Dam
Case 2: Ecological water supply in North China
As a reaction to the groundwater over-extraction problem in North China, the Ministry of Water Resources selected the Hutuo River, Fuyang River and Nanjuma River as the pilot rivers to implement ecological water replenishment of 1.32 billion cubic meters of freshwater from September 2018 to August 2019. Based on the experience from pilot rivers, the Ministry of Water Resources has expanded the ecological water supply to 21 rivers in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region since 2019. By the end of July 2021, a total of 11.39 billion cubic meters of ecological water replenishment had been implemented in North China. After the restoration projects were implemented, the ecosystem of river basins and lake basins improved significantly. There is a length of 1964 km rivers filled with fresh water and the water area reached 558 sq. km. The water quality at all of the monitoring sections has been greatly improved after the ecological water supplement.

Before and after comparison of ecological water supply
Case 3: Shanghai Qingxi Countryside Park
As one of the 21 countryside parks of Shanghai, the first phase project of Qingxi Countryside Park was built up in October 2016 and opened to the public. The countryside villages played an important role in leading the construction of Qingxi park. Its design followed the concept of integrating the water, forest, land, lake, grass, village and factory into one comprehensive project and focused on saving, protecting and recovering the natural environment and resources. Based on the existing rivers, arable land, forests and villages, this countryside park provides fruitful functions to Shanghai, the megacity, such as ecological restoration, science education, agricultural production, as well as leisure and recreation. Before this project, the Qingxi area was facing many serious ecological problems, including loss of wetland, disconnection of waterbody, pollution from agriculture and inefficient land use. Focusing on these problems, the project takes five strategies to implement ecological restoration, including wetland and waterbody recovery, river comprehensive realignment, agroecosystem management, careful land use planning and making space for science, leisure and culture. Now, the Qingxi Countryside Park has 0.8 hectares of new forest, 99.2 hectares of new agricultural land and 19.8 hectares of new waterbody. The beautiful environment attracted Huawei and many other high-tech companies to locate in this area.
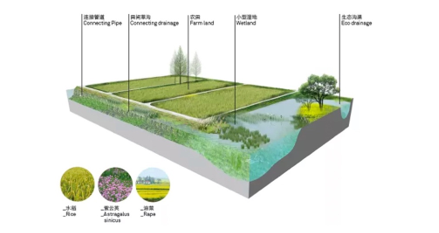
The agroecosystem management strategies of Qingxi Countryside Park
Case 4: Ecological Restoration of Lvjinhu Mined Area
Mining activities produced a lot of abandoned mine land. The mining subsidence area in Huaibei, Anhui Province is large, widely distributed and harmful to socio-economic development. To promote the ecological civilization, Huaibei City has put increasing efforts on ecological restoration of mining subsidence areas and achieved remarkable economic and social benefits. This case shows a good example of sustainable development of coal-resourced cities. Ecological restoration of Lvjinhu Mined Area is a key project for abandoned mine land management approved by the Ministry of Natural Resources (formerly the Ministry of Land and Resources) and the Ministry of Finance. This project used the PPP model to attract social capital and has successfully raised 2.22498 billion RMB. Financial issues usually are the big problem in ecological restoration projects, while this case creatively solved the financial problems and provide a new solution to manage mine subsidence area. After this project was implemented, there is 16.33 sq.km of new available land, 7.73 sq.km of new waterbody and 36,800,000 cubic meters freshwater storage. The abandoned mine land has been converted into a beautiful and ecological central city park.
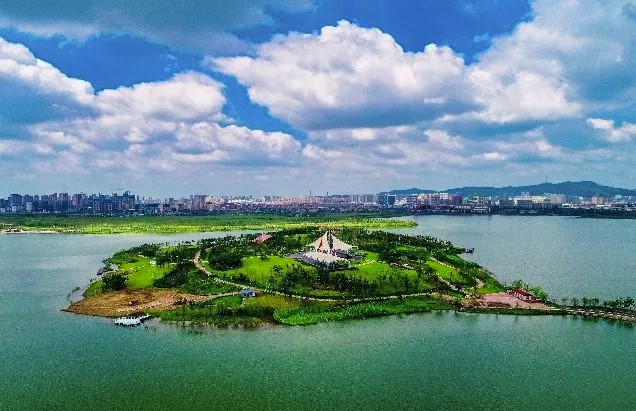

The Dream Island of Lvjinhu
Case 5: Soil Erosion Management in Changding County
Changding, located in Longyan City, Fujian Province, has a total population of 530,000 and a land area of 3099 sq. km. Due to human activities, topographical features, climate change and some historical reasons, Changding County was facing very serious soil erosion in the 1940s. It used to be one of the three key soil erosion areas of China. Changding County explored a new path to manage soil erosion that combined engineering methods and biological methods, artificial management and ecological restoration, ecological construction and economic development. Until 2020, an area of 760.84 sq. km soil erosion land has been converted, the erosion rate decrease by 6.78%. The forest rate increased to be 80.3% and the area of wetland reached 3513 hectares. Also, this ecological restoration project provides a lot of habitats for wild animals and plants. The beautiful natural environment brings more investments and economic growth to Changding. In 2020, this county had 1 million visitors from the tourism industry, receiving 1,166 million RMB income, and the disposable income of farmers reached 18,149 RMB per capita, with an average annual growth of 10.7%.

Before and after comparison of soil erosion management
Case 6: Desertification Combating in Zuoyu County
Zuoyu County, Shanxi Province, is located on the edge of the Mauusu Desert. In the 1950s, this county had only 5.33 sq.km of low-quality forest. The forest greening rate was less than 0.3%. The sanding land occupied 76% of the total area of Zuoyu County. In the past 70 years, the local government and people made great efforts to combat desertification and changed this county to be a green home. Based on the 1124 sq.km forests, Zuoyu County developed green and sustainable industries, such as seedling cultivation and ecological tourism. In 2020, 4,250,000 tourists visited Zuoyu County and contributed to 2.643 billion RMB tourism revenue.

Aerial view of Zuoyu County
Photos from the Ministry of Natural Resources(Wechat official account)
Source: <https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/6MbYcGZHvQ6_1InxgGI-Ww>
Edited and translated by Jia Mengyuan