


On July, 9th, the online forum, related to Urban Form and COVID-19: Thinking Through Issues of Density, Overcrowding, Public Space, and Health, was led by UN-Habitat and the World Health Organization(WHO). Mr. Nan Shi, Executive Vice Chairman and Secretary-General from Urban Planning Society of China, was invited to participate and deliver a speech on the relationship between urban density and disease transmission.
As part of the 2020 Meeting of the High-level Political Forum on Sustainable Development,the online forum, related to Urban Form and COVID-19: Thinking Through Issues of Density, Overcrowding, Public Space, and Health, was led by UN-Habitat and the World Health Organization(WHO) on Thursday, 9 July.
Mr. Nan Shi, Executive Vice Chairman and Secretary-General from Urban Planning Society of China, was invited to participate. Other participants include Maimunah Sharif, Under-Secretary-General and Executive Director of UN-Habitat, Naoko Yamamoto, Assistant Director General for the Healthier Populations Division of World Health Organization, Damià Calvet, Councillor of Territory and Sustainability of Regional Government of Catalonia(Spain) and Dr. Oxiris Barbot, Commissioner of Department of Health from City of New York (USA). The moderator is Christopher Williams, Director of New York Office of UN-Habitat.
As Member States review strategies to bolster local action to accelerate Agenda 2030 in an era of COVID19, they must consider the relationship between urban form and health. Some predict a withdraw from cities. Others note prior public health crises have brought about improved sanitation, streets and public spaces, and cities will continue to adapt and thrive. Underlying such thinking are assumptions about density and disease. Research shows the relationship is not direct: also important are housing conditions, income, health care, public space, and sanitation. The event will enable decision makers, urban planners and health professionals unpack these issues to bolster local action.

Maimunah Mohd Sharif, Executive Director, UN Human Settlements Programme (UN-Habitat)
In the speech, Maimona Mohad Sharif thinks that as COVID-19 has brought huge challenges to the city development ,the relationship between urban form and COVID-19 thus becomes the hot topic for everyone. And Almost all the countries now are paying great attention to how to make cities more effective to deal with the disaster events including COVID-19 and climate change. Meanwhile, other key points should also include the difficulties faced by slums and other informal living sites, health demands from vulnerable people in the cities and the community governance. Through the implementation of New Urban Agenda (NUA), she hopes that the global could reach a consensus and consider the city as a breakthrough point to deal with various challenges.
Naoko Yamamoto, Assistant Director General for the Healthier Populations Division of World Health Organization
In the speech, Naoko Yamamoto believes that city, as a kind of machine for production, should serve everyone’s welfare and well-being. City’s overcrowding might aggravate the dealing with COVID-19, which is more severe for those vulnerable groups and residents living in informal settlements. A healthy city need to benefit everyone and every place. And city should satisfy the demands of basic services, medical facilities and material supply from everyone, especially in the context of COVID-19. Meanwhile, public participation is very crucial for city development and governance, which enable everyone enjoy equal rights and thus promote sustainable developments.

Damià Calvet, Councillor of Territory and Sustainability of Regional Government of Catalonia,Spain
In the speech, Damià Calvet believes that the relationship between urban density and COVID-19 should be deeply explored and reviewed. The high density is necessary for city development, but it may create conditions for the spread of virus. However,city is also the key element to solve the problems. City density provides the convenience for management, which makes it possible to manage and control the lower administrative level including the communities.We should integrate multiple element, such as economy, health and culture, to therefore construct the sustainable city. Meanwhile, the whole world need to strengthen the consensus and work together to promote NUA.

Dr. Oxiris Barbot, Commissioner of Department of Health from City of New York ,USA
In the speech, Dr. Oxiris demonstrates the difficulties faced by New York in the COVID-19 prevention and control. High density of the city highlights the shortage of medical and sanitary resources, which also cause difficulties for those people isolated at home. Meanwhile, various gathering activities triggered by types of hot issues have brought potential threat, and thus COVID-19 prevention and control becomes more difficult, challenging city’s recovery to the normal operation.

Mr. Nan Shi, Executive Vice Chairman and Secretary-General from Urban Planning Society of China
In the speech, Mr. Nan Shi focuses on the relationship between city density and disease transmission. City density is the both the product of scale economy and agglomeration effect and the value of city existence. City density not only means the population density and development intensity, but also indicated the service density and accessibility of facilities. Through the comparison of population density and cumulative number of confirmed cases from macro, meso and micro perspective, Mr. Nan Shi points out that there’s no direct connection between population density and disease transmission, but intensity of contact is closely related to the disease transmission. Other integrated elements, which affect the prevention and control of COVID-19, include spatial distance, governance level and social consensus.
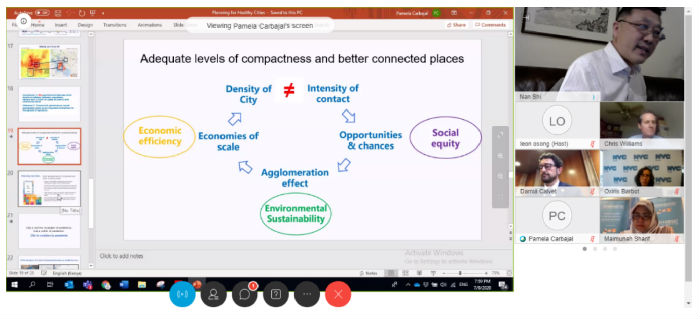
Key points of Mr. Shi Nan in the online forum
According to Nan Shi’s speech, what is needed is to fight epidemic is to reduce the contact, cut off the routes of transmission, rather then simply reducing the density. More exactly, city is also the victims of the epidemic and the key to achieve the prevention and control of COVID-19, not the cradle of infectious diseases. Under the guidance of international files, such as 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development and NUA, Policy makers, managers and planners of all countries should promote the cities more resilient, inclusive and healthy with the comprehensive and high-quality plannings.
The High-Level Political Forum on Sustainable Development (HLPF) is the main United Nations platform for follow-up and review of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. The HLPF provides political leadership, guidance and recommendations for sustainable development. It reviews progress in the implementation of the 2030 Agenda and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), with the aim to integrate the economic, social and environmental dimensions of sustainable development.The HLPF meets every year under the auspices of the UN Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC), and every four years under the auspices of the UN General Assembly, when Heads of State and/or Government attend the Forum.
In 2020, the HLPF under the auspices of ECOSOC was held on 7–16 July under the theme “Accelerated action and transformative pathways: realizing the decade of action and delivery for sustainable development”. The objectives include·focusing on bolstering local action for accelerating implementation of Agenda 2030, and in consideration of COVID-19.; sharing country experiences in responding to COVD-19 in different urban settings and density conditions; strengthening cooperation among policy makers, health professionals and the planning profession in the era of COVID-19 and beyond.
Translated by Wang Yue